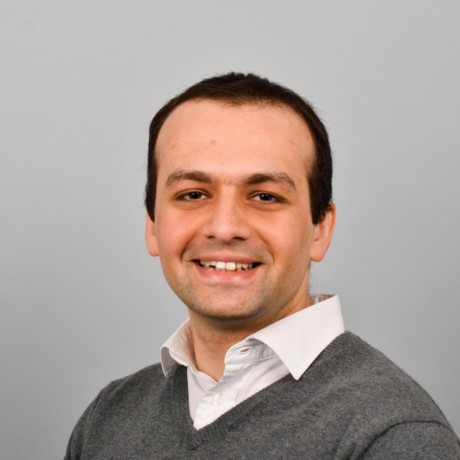
Configuring Slack Notifications for Google Cloud Build
- 6 minsAdding Slack notifications for your Google Cloud Build jobs explained with code examples and screenshots.
Intro
Recently we decided to migrate our builds from Travis CI to Google Cloud Build to speed up the builds. The process was quite easy and flawless; however, we were still missing a few minor things. One of them was the notifications from Cloud Build to our #ops channel in Slack. This was slightly annoying because you would not know if the build was finished and the site was deployed, or if it failed for some reason.
Integrating with Cloud Build was a bit more different than what you are used to from integrations with Jenkins or Travis CI. Normally you would just create a webhook that would call an interface in the Slack API. In Cloud Build, on the other hand, everything is getting posted to the Pub/Sub queue built into the platform, and here you would just need to subscribe to the specific queue and listen for the events. To achieve the latter, you would need a small serverless function to listen for these events and to call the Slack API.
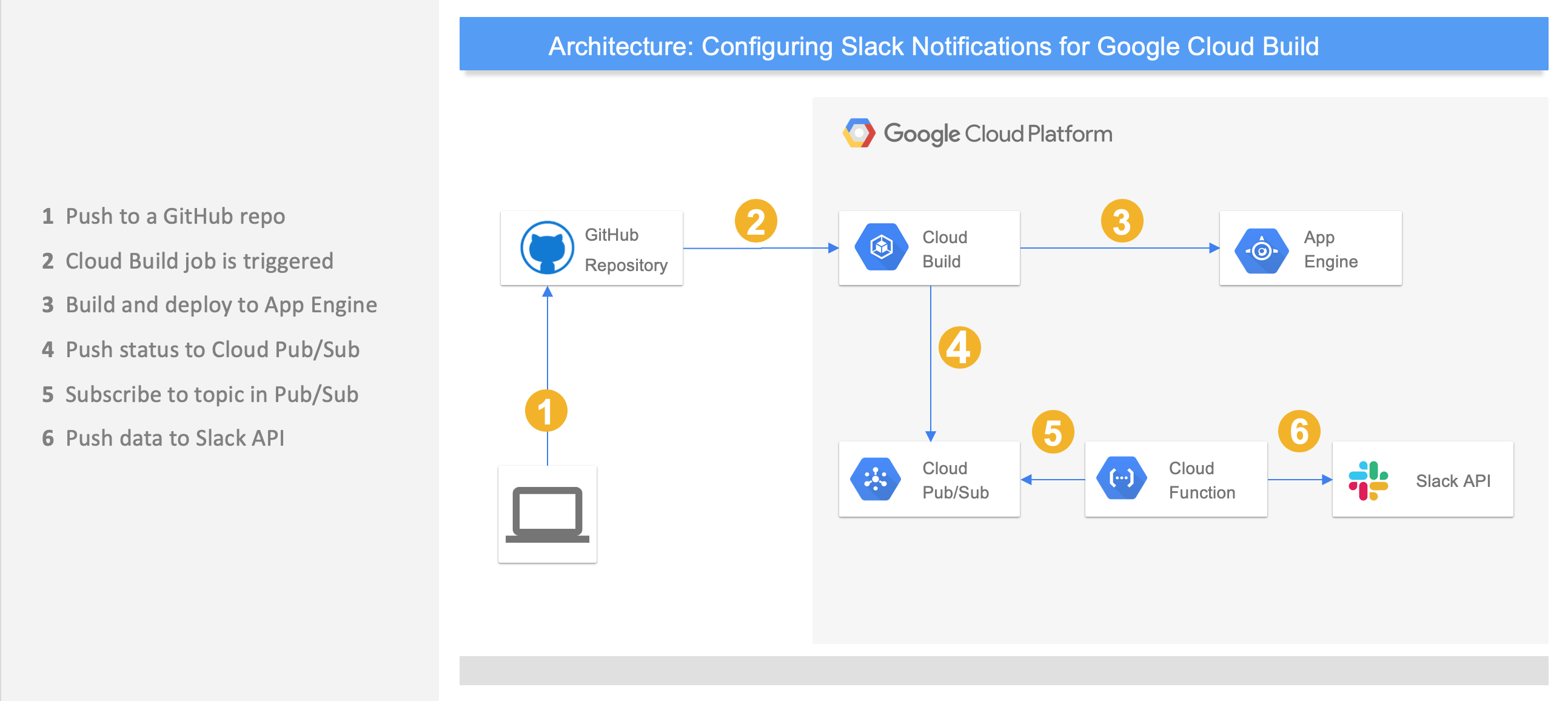
Note that here we will, technically, be using paid services on Google Cloud Platform, as both Cloud Build, Cloud Pub/Sub, and Cloud Functions are billable components. However, since all the components above provide a generous free tier, you will need to work hard to get passed the free tier with this setup.
- Cloud Build: Free first 120 builds-minutes per day for
Basicmachine type (n1-standard-1). - Cloud Pub/Sub: Free first 10GB per month (pricing).
- Cloud Functions: Free first 2 million invocations per month (pricing).
1. Before you begin
1.1 Prepare your GCP project
I assume you have a Google Cloud Account, and that you have signed in to your account.
- Select or create a Google Cloud Platform project, e.g. from the Manage resources page.
- Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud Platform project.
- Enable the Cloud Functions and Cloud Pub/Sub. You can also enable the APIs using this link.
- Use Cloud Shell right from the browser, or you can Install and initialize the Cloud SDK on your own machine.
- If you have installed the Cloud SDK, update and install gcloud components:
gcloud components update &&
gcloud components install alpha beta1.2 Prepare your Slack App
I assume you have Slack installed and that you have created and signed-in to your account.
Create a new Slack app:
- Choose the app’s name and your Slack team. Click Create.
- Click Incoming Webhooks.
- Activate incoming webhooks.
- Click Add New Webhook to Workspace. An authorization page opens.
- From the drop-down menu, select the channel to which you would like notifications sent.
- Click Authorize.
- A webhook for your Slack application has been created. Copy the webhook URL and save it for later use.
2. Create a Cloud Function
We need to create a Cloud Storage bucket to stage your Cloud Functions files. Use [STAGING_BUCKET_NAME] that is a globally-unique bucket name (such as [PROJECT-ID]_cloudbuilds):
gsutil mb gs://[STAGING_BUCKET_NAME]You should see the following output:
Creating gs://[PROJECT-ID]_cloudbuilds/[STAGING_BUCKET_NAME]...Next, create a directory on your local system for the application code:
mkdir ~/gcb_slack
cd ~/gcb_slackThen, create the following two files in the gcb_slack directory.
File 1: package.json
{
"name": "google-container-slack",
"version": "0.0.1",
"description": "Slack integration for Google Cloud Build, using Google Cloud Functions",
"main": "index.js",
"dependencies": {
"@slack/client": "4.10.0"
}
}File 2: index.js
Note: Make sure to update SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL in the code below.
const IncomingWebhook = require('@slack/client').IncomingWebhook;
const SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL = "<INSERT YOUR WEBHOOK FROM STEP 1.2>"
const webhook = new IncomingWebhook(SLACK_WEBHOOK_URL);
// subscribe is the main function called by Cloud Functions.
module.exports.subscribe = (event, callback) => {
const build = eventToBuild(event.data.data);
// Skip if the current status is not in the status list.
// Add additional statues to list if you'd like:
// QUEUED, WORKING, SUCCESS, FAILURE,
// INTERNAL_ERROR, TIMEOUT, CANCELLED
const status = ['SUCCESS', 'FAILURE', 'INTERNAL_ERROR', 'TIMEOUT'];
if (status.indexOf(build.status) === -1) {
return callback();
}
// Send message to Slack.
const message = createSlackMessage(build);
webhook.send(message, callback);
};
// eventToBuild transforms pubsub event message to a build object.
const eventToBuild = (data) => {
return JSON.parse(new Buffer(data, 'base64').toString());
}
// createSlackMessage create a message from a build object.
const createSlackMessage = (build) => {
let message = {
text: `Build \`${build.id}\``,
mrkdwn: true,
attachments: [
{
title: 'Build logs - Your Custom Message Goes Here',
title_link: build.logUrl,
fields: [{
title: 'Status',
value: build.status
}]
}
]
};
return message
}3. Deploy the Cloud Function
To deploy the subscribe function with a Cloud Pub/Sub trigger, run the following command in the gcb_slack directory:
gcloud functions deploy subscribe --stage-bucket [STAGING_BUCKET_NAME] \
--trigger-topic cloud-buildswhere [STAGING_BUCKET_NAME] is the name of your staging Cloud Storage Bucket that you defined earlier.
You should see an output confirming the creation of the cloud function and status: READY.
After you’ve completed deployment of the Cloud Function, when a build event occurs, you will receive a Slack notification.
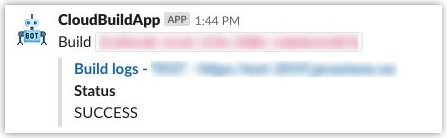
Also, feel free to customize your app, like adding a custom icon, as I did with mine. ☝️
